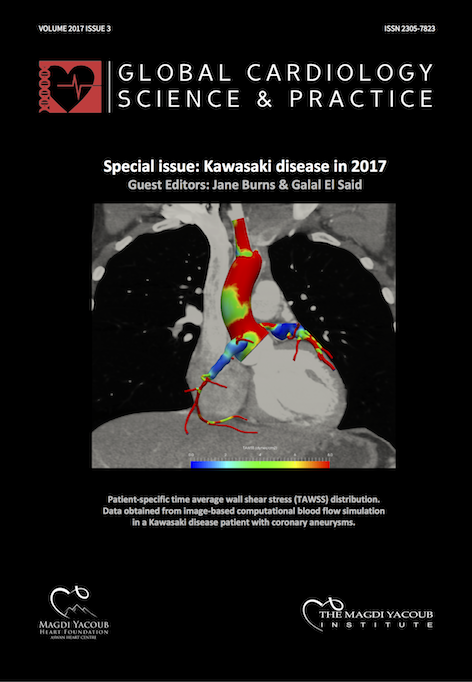
Computed tomography coronary angiography is the way forward for evaluation of children with Kawasaki disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21542/gcsp.2017.28Abstract
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute idiopathic vasculitis affecting infants and children. Coronary artery abnormalities and myocarditis are the major cardiovascular complications of KD. Coronary artery abnormalities develop in 15–25% of untreated KD. Two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography has hitherto been considered the modality of choice for evaluation of children with KD. There are, however, several limitations inherent to echocardiography - including limited evaluation of distal vessels, left circumflex artery and poor acoustic window in growing children. Catheter angiography is the gold standard for evaluation of coronary artery abnormalities in older children and adults; however it also has inherent limitations - including complications related to its invasive nature, higher radiation exposure, and inability to evaluate intramural abnormalities. Thus serial invasive coronary angiography studies are not feasible in children. There have been major advances in computed tomography (CT) coronary imaging so that it is now possible to delineate the coronary artery anatomy with higher temporal resolution and motion-free images at all heart rates with acceptable radiation exposure. There is, however, a paucity of literature with regard to the use of this technique in children with KD. In this review, we discuss the application of computed tomography coronary angiography (CTCA) in children with KD with special reference to strategies aimed at reducing the effective radiation dose.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license CC BY 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.